Last Mile Delivery, E-Commerce, and Mobile Warehousing
Many forecast that American consumers would huddle in their homes and hoard their money during the COVID lockdown. As it turned out, that was not always the case. COVID-19 was a game changer.
The Rise of Ecommerce
With the retreat to home, American consumers invested in their personal environments, choosing instead, to make them more serviceable, comfortable, and suitable for work, home schooling and a retreat for the family. Renovations, upgrades in finishes such as flooring and other materials helped to fuel the success of the construction trade and home improvement store retailers.
Home Depot, for example, reported an increase of 25.1 percent year over year in Q4 2020 with a net income increase of 15 percent in the same quarter the previous year. By comparison, Lowe’s reported a 27 percent increase in net sales in Q4 2020 in comparison with an increase of 28.6 percent by other U.S. industry competitors. Ecommerce sales seem to have played a major role in the increases.
Other industries saw similar upticks in business. With Americans sheltering in place, buying patterns shifted from in-store retail to buying online and home delivery. With the new need for higher volume, more frequent deliveries, warehousing, transportation, and the supply chain needed to be changed.
From the City to the Country?
Did you know that the U.S. Census Bureau reported that 29.8 million Americans, approximately 9.3 percent of the population moved homes in 2019? Studies show a tendency for Americans to move away from urban centers into rural or suburban areas. Recently, research has indicated a potentially larger shift in this same direction but is not yet considered definitive.
This may have been facilitated by the trend towards remote working. As much of the country’s workers did not report to work in person in offices much of last year, companies had the opportunity to study the issue of remote work and to determine its impact on productivity, responsiveness, and profitability.
A two-year study conducted by Great Place to Work® surveyed 715 companies representing over 3 million American employees and produced 800,000 responses. Employee productivity was measured from March to August of 2020 and compared to the same period in 2019. The results of the study indicated that workforce productivity improved while working from home.
New studies in 2021 indicate that a major shift from cities to suburban and rural areas may be underway. Over 20 percent of Americans either moved during the pandemic or know someone who did. Americans are migrating to cities with affordable housing and living expenses, away from large metropolitan areas and urban business centers. The top four states from which Americans moved in 2020, California, Illinois, New York, and the District of Columbia are listed among the 15 most densely populated states.
Where are all these people moving to establish new homes? Most Americans, approximately 90 percent of those who moved in 2020, in fact, remained in the same county.
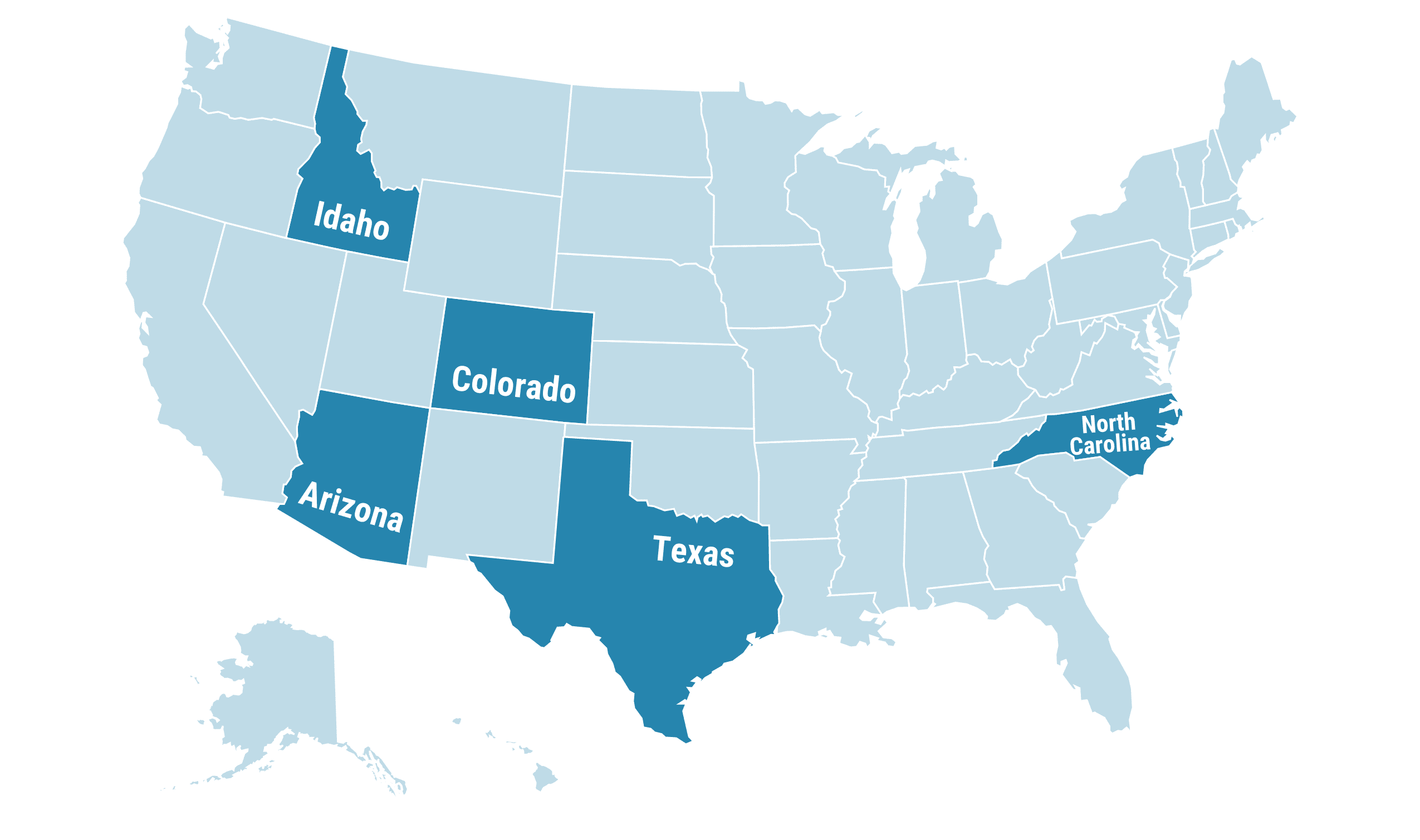
Here are the top states that experienced the most population growth in 2020:
- Arizona
- Colorado
- Idaho
- North Carolina
- Texas
The Importance of Population Migration to Last Mile Delivery
When people are closely to each other and in densely populated areas, delivering huge volumes of packages rapidly is easier and faster. This is because package recipients are more likely to live closer to each other. Less travel=less time spent in delivering goods and lower shipping costs.
As Americans navigate the New Normal and move further away from each other, supply chain businesses must consider this and carefully plan new strategies to optimize efficiencies, reduce travel time and keep costs under control. Having warehouses, distribution centers and fulfillment centers in optimal locations adjacent to population centers has been instrumental in the last mile delivery logistics process to date.
Volume density, having more parcels to deliver to one location or one nearby is an important principle to last mile delivery providers. Having volume density means that more packages can be delivered in a smaller area, keeping travel time and shipping costs down. In suburban areas, however, houses and businesses tend to be farther away from each other.
In areas where consumers and businesses are more spread out, it makes more sense for many last mile delivery companies to outsource package delivery to the United States Postal Service (USPS) as it is already responsible for mail delivery to those locations. Route optimization and reduced costs have resulted in FedEx in-sourcing most of its SmartPost parcels. The company has renamed the service FedEx Ground Economy. UPS re-strategized 41 percent of its SurePost volumes inside the UPS network.
New Last Mile Delivery and Alternative Delivery Strategies
Traditional supply chain methods rely on human-operated delivery vehicles for last mile delivery. This is partially because there is a high volume of deliveries, requiring continual dispensation of parcels from the vehicle. Last mile delivery is the most expensive part of the transportation and logistics process.
With the need for an expanded range of alternative last mile delivery options, companies are exploring other opportunities for change. We need more delivery solutions. From third party logistics providers that specialize in e-commerce rapid order fulfillment to transportation hubs that service the industry and the delivery drivers that work hard every day to ensure faster deliveries, new ideas are continually needed to help ensure customer expectations are met.
Solve the Last Mile
Here are some other last mile logistics strategies being used:
- Self-collection by consumers of the ordered items either at specified pick up points, parcel lockers or similar options.
- Collaboration with retailers, a strategy pioneered by Amazon and Kohl’s proved to be a way for FedEx to expand its reach to suburban and rural areas. Dollar General has 14,000 stores in 44 states, primarily in smaller or mid-sized communities. By partnering with FedEx, Dollar General can generate foot traffic for its stores while accepting deliveries and returns for FedEx. This eliminates the need for FedEx to deliver goods to all rural and suburban homes and businesses. Other retail partnerships exist between UPS and Michael’s, CVS and AutoParts and function in a similar manner.
- Crowdsourcing last mile logistics can be effective, especially when the delivery cost is high. Crowdsourced delivery is not necessarily available in all areas but can provide needed flexibility needed to expedite deliveries to help ensure that customer expectations are met.
- Reception boxes kept in consumers’ homes and accessible by delivery personnel can be effective for order deliveries for which the customer cannot be present.
- Drones and robots may be utilized to supplement or replace human labor, taking goods from the trucks and delivering them to customers.
What is a Mobile Warehouse and How Does It Work?
Inspired by vending carts used for many years to transport fruits and vegetables from street to street in cities, mobile warehouses show promise in solving the problem of last mile logistics. Typically, trucks are used as mobile warehouses and are assigned to specific geographical locations. Each mobile warehouse stores goods that have been selected to help meet the demand in that respective area. This enables companies to pre-position high demand goods so that the inventory can be sold quickly. This can be done for popular product launches, fast moving SKUs and other types of inventory.
Mobile warehouses can pick up enough inventory for a discrete time period from a stationary warehouse situated outside the city then quickly travel into the city throughout the day to facilitate deliveries within an hour of order placement. In an alternative scenario, the mobile warehouse may interface with other neighboring mobile warehouses or the distribution unit to facilitate product delivery to customers.
Moving past the COVID pandemic, the mobile warehouse strategy can also prove effective. In dealing with products that are unavailable in the mobile warehouse, this can be remedied by gaining replenishment from the nearest mobile warehouse or distribution unit, although this may take a bit more time.
Success of the mobile warehouse strategy is dependent upon its ability to fulfill orders based on the inventory available within the truck used as a warehouse. Business intelligence plays a vital role in predicting the demand in each specific geographic area. Mobile warehouses stock up on the variety of goods that meet the demand profile in the specified area so that they can fulfill orders in real time. Having accurate demand forecasting is crucial.
Mobile warehouses have gained popularity over the past year and will undoubtedly be put to new use to deal with the changing distribution of the U.S. population. So far, mobile warehousing has shown itself to be a useful tool in expediting deliveries, meeting customer expectations for same day delivery and keeping shipping costs under control.
As the trend continues, smart technology, warehouse management technology solutions, transportation management and route planning will be utilized to optimize the effectiveness of mobile warehousing.
Why Mobile Warehousing is Gaining Popularity
- Provides flexible, scalable warehouse space
- Enables the forward deployment of inventory
- Facilitates greater supply chain resiliency
- Helps accommodate changing consumer behavior
- Provides a new way to mitigate supply chain risk
- Reduces the distance of the shipper’s supply chain relative to the end-user
- Facilitates rapid delivery options
- Reduces stress on transportation and delivery systems
- Decreases shipping cost due to proximity of inventory to customers
- Can act as a replacement or supplement to zone skipping for parcel and LTL moves
Conclusion
The introduction of online shopping years ago was predicted to be a game changer, and it has been, especially as it rocketed to success over the past year. As brick and mortar retailers and the gig economy suffered, consumers needed new ways to buy online and get goods delivered to their homes.
As Americans migrate to more sparsely populated areas, last mile delivery to final destinations is proving extremely challenging, time consuming and costly. Shipping costs are rising. Distribution centers, warehouses and fulfillment centers are located closer to urban populations and are challenged to keep costs under control while meeting the dynamic expectations of customers.
Keeping operational costs as well as shipping costs under control can be challenging in dealing with warehouses or distribution centers, especially those that provide last mile delivery. Using technology platforms, route planning and route optimization can be helpful in this regard.
Leveraging mobile warehouses can provide the added flexibility and scalability needed for final mile deliveries in a variety of circumstances and can help meet logistical challenges. Use of mobile warehouses can help facilitate faster deliveries, improved brand loyalty (as consumers have identified this is linked to meeting customer expectations for order delivery).
Today, meeting the biggest challenges in the supply chain takes a combination of creativity, innovation, technology, and perseverance. From re-inventing delivery service providers (now crowdsourced) to robotic delivery to each customer’s doorstep, last mile delivery providers and warehouses are on the cutting edge, working hard every day to keep us fully stocked with toilet paper and all the essentials. We thank them every day for it!
What Makes Datex Different?
1. Revolutionary low code/no code flexible workflow-driven warehouse management software
2. Most configurable, user-friendly WMS on the market today
3. End-to-end solution provider: software, hardware, EDI, and managed services
4. White Glove Concierge Service
5. Executive-level attention and oversight






